Best Approaches for Managing Inflammatory Airway Diseases: An Evidence-Based Guide for Physicians
Introduction: The Growing Burden of Inflammatory Airway Diseases
Inflammatory airway diseases (IADs)—including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis, and chronic bronchitis—affect over 500 million people worldwide (Global Burden of Disease Study, 2023). Despite treatment advances, 40% of patients remain poorly controlled, leading to increased hospitalizations and healthcare costs.
For physicians, staying updated on precision diagnostics, emerging biologics, and digital health tools is critical to improving outcomes. This comprehensive, evidence-based guide covers the latest strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of IADs in 2024.
Understanding the Basics: What Are Inflammatory Airway Diseases?
Inflammatory airway diseases (IADS) are characterized by chronic airway inflammation, resulting in symptoms such as wheezing, cough, dyspnea or shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Asthma typically presents with reversible airway obstruction and is often driven by allergy or hypersensitivity mechanisms. In contrast, COPD is marked by progressive, irreversible airflow limitation, most commonly associated with smoking or chronic environmental exposures.
Key features and primary triggers of inflammatory airway diseases:
| Condition | Key Features | Primary Triggers |
|---|---|---|
| Asthma | Reversible Obstruction, Eosinophilic Inflammation | Allergens, Infections, Exercise, Cold air |
| COPD | Irreversible Airflow Limitation, Neutrophilic Inflammation | Smoking, Pollution |
| Bronchiectasis | Chronic Mucus Retention, Recurrent Infections | Postinfection, Autoimmune Diseases, Genetic Disorders like Cystic Fibrosis |
Despite their distinct clinical and pathophysiological features, many patients may present with symptoms from more than one condition, requiring a dual-pathway or combined therapeutic approach.
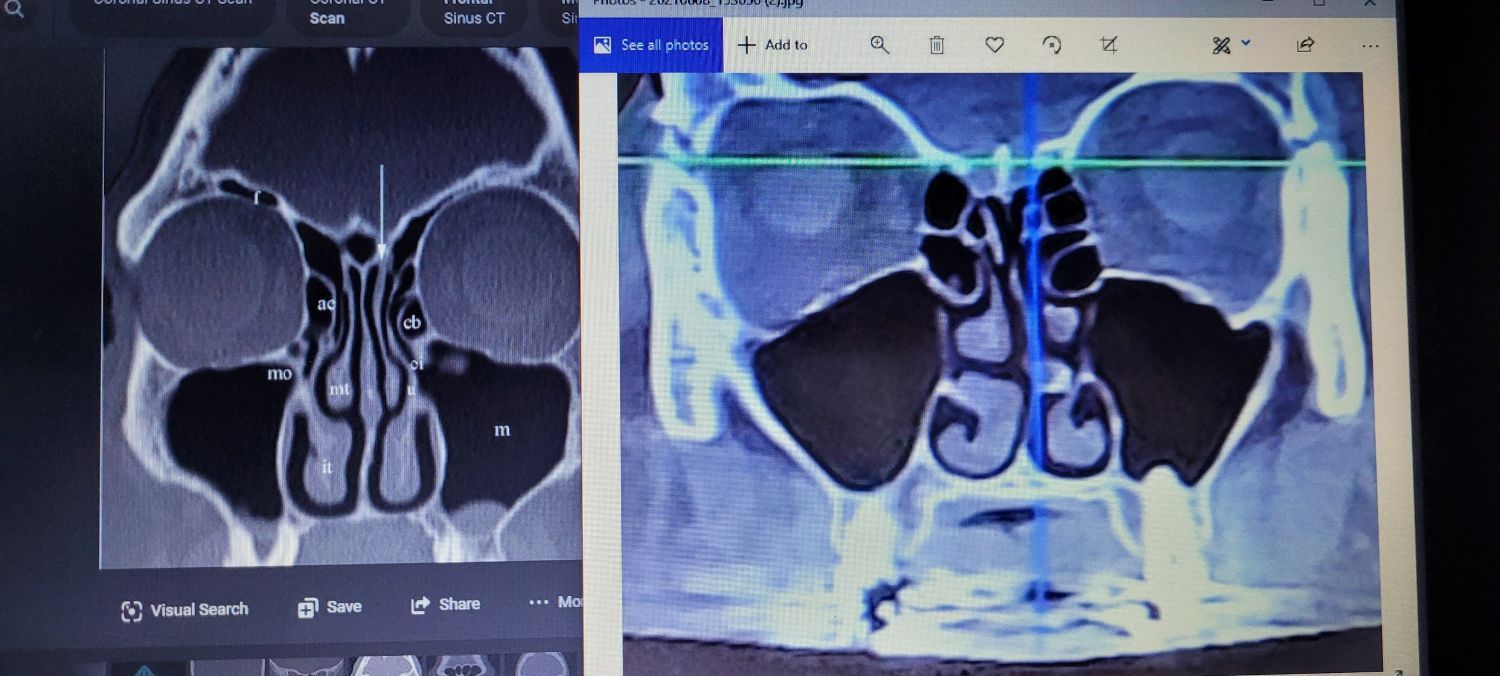
Phenotype-Driven Diagnosis: Beyond Spirometry
Phenotype-driven diagnosis goes beyond traditional spirometry by identifying distinct clinical and biological characteristics in patients, allowing for more personalized and effective treatment of respiratory diseases.
Essential Diagnostic Tools for IADs
| Test | Best For | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| FeNO (≥25 ppb) | Eosinophilic Asthma | Predicts Steroid Response |
| Blood Eosinophils (≥150 cells/μL) | Type 2 Inflammation | Guides Biologic Therapy |
| HRCT Chest | Bronchiectasis, Emphysema | Detects Structural Damage |
| Sputum Culture | Chronic Pseudomonas/NTM Infections | Directs Antibiotic Therapy |
Helpful Tip: A FeNO level greater than 50 ppb indicates a 90% likelihood of steroid-responsive asthma. In COPD patients, blood eosinophil counts of 300/μL or higher suggest a positive response to inhaled corticosteroids (ICS).
Pharmacotherapy Updates: 2024 Guideline
Here are the 2024 pharmacotherapy updates for physicians:
For asthma, mild cases can be treated with as-needed ICS-formoterol, based on recent research. Moderate to severe asthma is best managed with triple therapy, combining an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS), a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), and a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA). For severe type 2 asthma, biologic treatments or anti-IgE can reduce flare-ups by more than 50%.
In COPD treatment, the first choice is a combination of LAMA and LABA. Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) should be added if blood eosinophil counts are 300/μL or higher, or if the patient has frequent flare-ups. For those with chronic bronchitis, roflumilast may be helpful.
For bronchiectasis, macrolide antibiotics such as azithromycin help lower the number of flare-ups. Nebulized antibiotics like colistin or tobramycin are used to treat infections caused by Pseudomonas bacteria. Mucolytics like hypertonic saline can help clear mucus from the airways.
When Should You Think About Using Biologics?
- If your patient has two or more flare-ups a year despite being on high-dose ICS/LABA (GINA 2024 Update_See Section 5: Severe Asthma Management)
- If they show signs of Type 2 inflammation, like a FeNO level of 25 or higher or eosinophils above 150
- If they have allergic asthma with IgE levels over 30 IU/mL
Helpful tip:
Tezepelumab has been shown to reduce exacerbations even in patients with non-Type 2 asthma, according to the PATHWAY trial—so it might be worth considering in those cases.
Nonpharmacologic Interventions
Proven Adjunct Therapies
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation reduces dyspnea in COPD patients.
- Airway clearance devices help decrease infections in bronchiectasis.
- For smoking cessation, varenicline combined with counseling has the highest success rate.
Helpful tip:
Digital inhaler sensors improve medication adherence by 58%,
Managing Treatment-Resistant Respiratory Cases: A Step-by-Step Approach
Effectively managing treatment-resistant respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD requires a systematic approach.
Start by confirming the diagnosis and ruling out common mimics like vocal cord dysfunction (VCD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and cardiac conditions.
Next, optimize medication delivery by assessing and improving inhaler techniques, which can be easily monitored using video apps for better patient compliance. It’s important to evaluate and manage comorbidities, especially obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), as it can significantly worsen asthma and COPD control.
If symptoms persist without improvement after 4 to 6 months, consider switching biologic therapies to find a more effective treatment option.
Helpful tip:
Patients experiencing frequent pneumonias should be screened for underlying immunodeficiency, including IgG subclass deficiencies, to address potential causes of recurrent infections.
Breakthrough Therapies in the 2024-2025 Pipeline
The treatment landscape for inflammatory airway diseases is advancing quickly, with several exciting innovations on the horizon:
1. IL-33 Inhibitors (Itepekimab) – A Potential Breakthrough for COPD
- Target: The IL-33/ST2 pathway, a key driver of neutrophilic inflammation in COPD
- Timeline: Phase III trials are ongoing, with potential approval expected by 2025.
2. Gene Therapy for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
- Approach: CRISPR-based liver-directed gene editing offers a breakthrough way to correct the genetic defect causing the disease.
3. AI-Powered Exacerbation Prediction (Google DeepMind & NHS Collaboration)
- Technology: Combines electronic health record (EHR) data with wearable device metrics like oxygen saturation and cough frequency
- Performance: Predicts exacerbations around 7 days before any symptoms appeared
- Impact: A pilot study showed a 33% reduction in COPD hospitalizations, with a planned NHS rollout in 2025.
These advances promise to improve patient outcomes significantly by targeting disease mechanisms more precisely and enabling proactive management.
A Multidisciplinary Approach for Better Outcomes
A collaborative, multidisciplinary approach helps close gaps in care, reduce hospitalizations, and tailor treatments to each patient’s unique phenotype. This ensures patients receive precise, personalized medicine instead of fragmented care. By bringing together experts from different fields, these teams can effectively manage symptoms in the short term while working toward long-term disease control—ultimately improving the quality of life for those with chronic respiratory conditions.
Stay tuned for more insights from our Snot Force Team! At Snot Force Alliance, we actively engage in research collaborations and other initiative to keep advancing our field. Don’t miss out, register now for our upcoming 2025 annual meeting!