The Critical Role of Airway Management in Anaphylactic Shock
Anaphylactic shock is a severe and potentially fatal allergic reaction that can strike suddenly, making swift medical response crucial. For physicians, mastering airway management in these urgent situations is key to safeguarding patient lives and enhancing recovery outcomes.
In this blog, we will dive into the critical importance of effective airway management during anaphylactic shock. We’ll back our insights with compelling statistics and clinical guidelines that highlight best practices. Join us as we uncover strategies that can make a real difference in emergency settings!
Understanding Anaphylactic Shock
Anaphylaxis is characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms that can involve multiple organ systems, including the respiratory, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal systems. The most alarming aspect of anaphylaxis is its potential to cause airway obstruction due to edema and bronchospasm. According to the World Allergy Organization, the prevalence of anaphylaxis is increasing globally, with studies indicating that up to 2% of the population may experience anaphylaxis at some point in their lives.
Statistics and Epidemiology
- Incidence: A study shows a 21 % increase in emergency department visits related to food-induced anaphylaxis during the length of the study.
- Mortality: Lethal anaphylaxis occurs in about 0.65 to 2% of severe anaphylaxis cases, which means it results in 1 to 3 deaths for every million people.
- Common Triggers: The most common triggers for anaphylaxis include food allergens (e.g., peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish), insect stings, medications, and latex. Understanding these triggers is crucial for prevention and management.
The Importance of Airway Management
Airway management is paramount in the context of anaphylactic shock due to the following reasons:
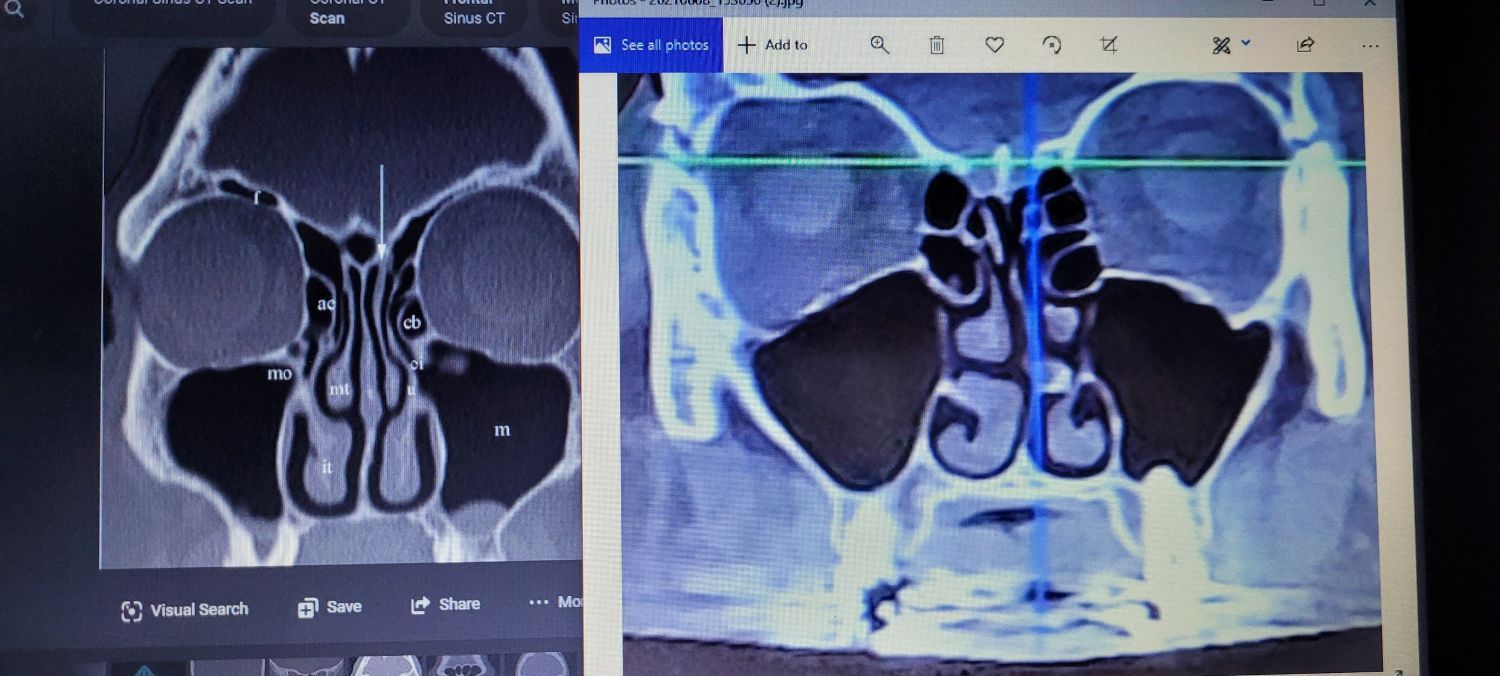
- Risk of Airway Obstruction: Anaphylaxis can lead to rapid swelling of the throat and tongue, resulting in potential airway obstruction. Fifty percent of patients with anaphylaxis experience upper airway edema, which can compromise ventilation.
- Bronchospasm: Anaphylaxis is often accompanied by bronchospasm, which can lead to wheezing, coughing, and respiratory distress. Effective airway management can help ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation during this critical time.
- Rapid Intervention: Immediate recognition and management of airway compromise can significantly improve patient outcomes. The use of supplemental oxygen, bronchodilators, and, in severe cases, advanced airway interventions may be necessary.
Guidelines for Airway Management in Anaphylaxis
The following guidelines can assist physicians in effectively managing the airway during anaphylactic shock:
- Assessment: Quickly assess the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs). Look for signs of respiratory distress, stridor, or inability to speak.
- Positioning: Position the patient in a way that facilitates breathing, typically in a sitting or semi-reclined position, unless contraindicated by other injuries.
- Administer Epinephrine: Epinephrine is the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis. Administering intramuscular epinephrine can rapidly reverse airway edema and bronchospasm. The AAAAI recommends a dose of 0.3 to 0.5 mg (0.3 to 0.5 mL of a 1:1000 solution) for adults, with repeat doses every 5 to 15 minutes as needed.
- Supplemental Oxygen: Provide supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate oxygen saturation levels. Monitor the patient’s vital signs closely.
- Advanced Airway Management: If the patient exhibits signs of severe airway obstruction or respiratory failure, be prepared to perform advanced airway management, such as intubation or cricothyrotomy, as a last resort.
Airway management plays a critical role in the treatment of anaphylactic shock. Given the increasing incidence of anaphylaxis and its associated risks, physicians must be equipped with the knowledge and skills to effectively manage the airway in these emergency situations. Prompt recognition, appropriate interventions, and a thorough understanding of the potential complications can significantly enhance patient outcomes and save lives.
Work alongside diverse clinicians, researchers, and healthcare professionals to enhance outcomes for airway conditions. Join our Snot Force Alliance team and contribute to meaningful change!