Understanding the Impact of Cognitive Dysfunction in Chronic Rhinosinusitis on Patients
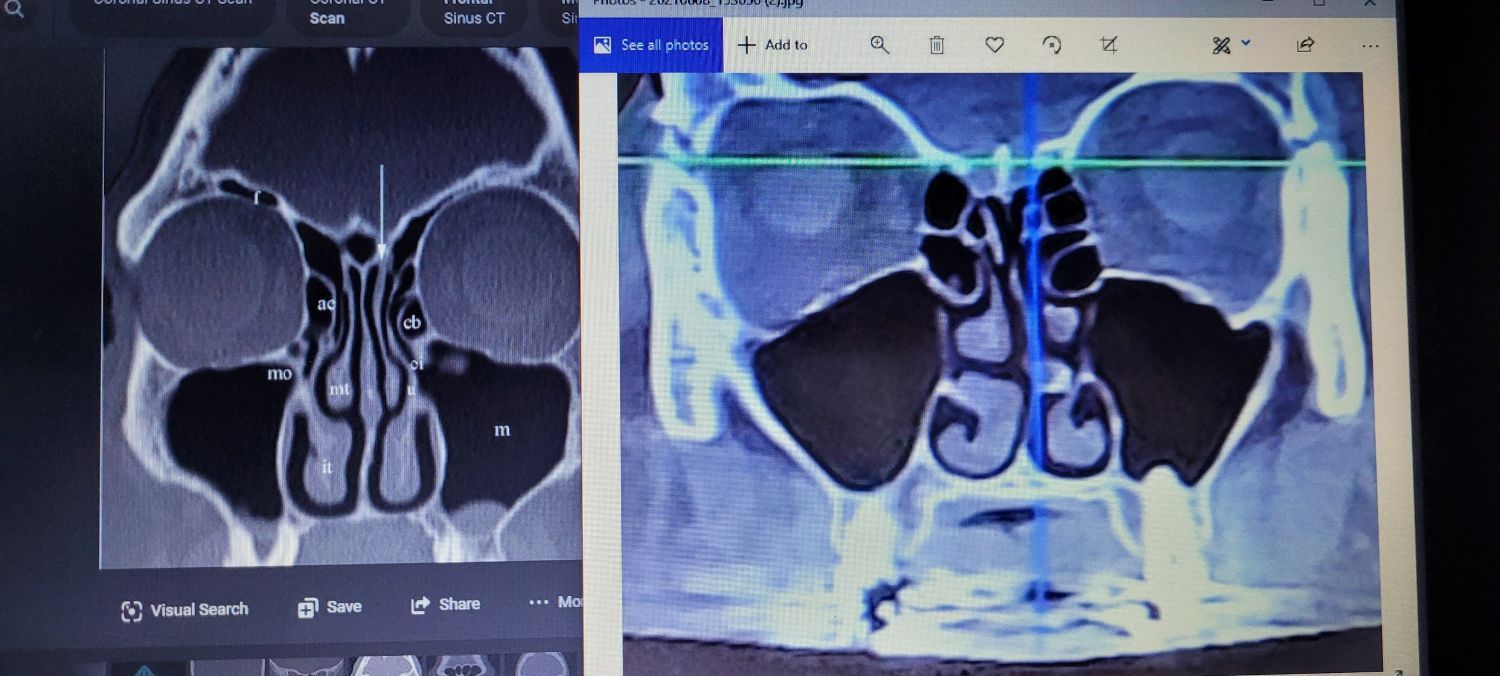
Did you know that chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) can affect more than just the sinuses? While the physical symptoms of CRS—such as nasal obstruction, facial pain, and purulent nasal discharge—are well-documented, the cognitive implications of this condition are less commonly discussed. This blog aims to inform physicians about the cognitive impacts.
Cognitive Dysfunction in CRS Patients
Recent studies have shown that patients with CRS often experience cognitive deficits that can include:
- Attention Deficits: Difficulty sustaining focus during tasks
- Memory Impairments: Challenges in both short-term and long-term memory retention
- Executive Functioning Issues: Problems with planning, organizing, and executing tasks
Mechanisms Behind Cognitive Dysfunction
Several mechanisms may contribute to cognitive dysfunction in CRS patients:
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammation may lead to changes in brain function and structure. Cytokines released during inflammatory responses can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect neuronal activity.
- Sleep Disturbances: Patients with CRS often suffer from sleep apnea or other sleep-related disorders, which can exacerbate cognitive impairments due to poor sleep quality.
- Reduced Oxygenation: Nasal obstruction can lead to hypoxia, which negatively impacts brain function.
Impact of Chronic Rhinosinusitis on Quality of Life
Cognitive dysfunction can significantly affect the overall quality of life of CRS patients. Key areas include:
- Work Challenges: Cognitive deficits can result in decreased job performance, absenteeism, and potential career setbacks, affecting financial stability.
- Social Relationships: Difficulty with communication and memory can strain relationships with family and friends, leading to social isolation.
- Mental Health: The frustration of dealing with cognitive issues can lead to anxiety and depression, further complicating the clinical picture.
Assessment and Management
Assessment
Physicians should consider incorporating regular cognitive assessments into the management plan for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) to better understand and address cognitive dysfunction. Tools such as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) or Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) can be useful for screening. Early detection allows for timely interventions.
Management Strategies
- Medical Management: Addressing the underlying inflammation through medications such as intranasal corticosteroids or antibiotics is crucial.
- Surgical Interventions: For patients with CRSwNP, endoscopic sinus surgery may alleviate symptoms and improve cognitive function.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Referral to neuropsychology for cognitive rehabilitation can help patients develop strategies to cope with memory and attention deficits.
By recognizing the cognitive aspects of chronic rhinosinusitis, physicians can offer more holistic treatment approaches that address both physical and mental health needs. Join the Snot Force Alliance to help research the connection between CRS and cognitive function. Together, we can discover effective ways to manage this condition and improve the quality of life for those affected.