Clinical Recognition of Acute Rhinosinusitis: Key Symptoms and Management Pathways
Acute rhinosinusitis (ARS) is a common clinical presentation, yet its symptoms can overlap significantly with protracted upper respiratory infections (URIs) and allergic rhinitis, complicating timely diagnosis. Accurate identification is important for implementing appropriate management and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions.
Pathophysiology and Etiology
ARS is characterized by inflammation of the paranasal sinuses lasting less than 4 weeks. The dominant etiology is viral. Inflammation leads to osteomeatal complex obstruction, mucociliary dysfunction, and retained secretions that create an environment for viral or, less commonly, bacterial proliferation. Common precipitating factors include preceding viral URIs and exacerbations of allergic inflammation.
Cardinal Symptoms for Clinical Diagnosis
The diagnosis of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis (ABRS) is primarily clinical, based on the presence of specific "cardinal" symptoms. The following eight signs are central to evaluation:
1. Nasal Obstruction/Congestion: Persistent, often bilateral nasal blockage is a hallmark. Patients may report worsening recumbency and the presence of purulent or mucopurulent anterior/posterior nasal discharge.
2. Facial Pain/Pressure/Fullness: Pain localized to the maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, or sphenoid sinus distributions is common. Pain may refer to the upper dentition (via the superior alveolar nerves) or manifest as otalgia due to referred pharyngeal pressure. Symptoms often exacerbate with Valsalva maneuver or forward flexion.
3. Cough: Typically, this is a secondary symptom driven by postnasal drip (PND). This cough is frequently more pronounced in the morning due to nocturnal mucus accumulation and can persist as a post-inflammatory cough after resolution of acute sinusitis.
4. Facial Headache/Pain: A frontal or maxillary headache that follows a diurnal pattern, often peaking in the morning and improving throughout the day, is suggestive. It must be distinguished from migraine, tension, and other primary headache disorders.
5. Hyposmia/Anosmia: Conductive smell loss occurs due to inflammatory obstruction of the olfactory cleft. This often leads to concomitant dysgeusia or hypogeusia.
6. Fatigue/Malaise: A non-specific but frequently reported systemic symptom related to the inflammatory cytokine response.
7. Fever: Low-grade fever may be present in both viral and bacterial ARS. High-grade fever (>39°C / 102.2°F) is more suggestive of bacterial etiology but is not a sensitive indicator.
8. Halitosis: This is caused by the presence of anaerobic bacterial byproducts and stagnant purulent secretions in the nasal passages.
Clinical Management and Specialist Referral
While most ARS cases are viral and self-limiting, symptom control and accurate identification of bacterial cases are essential. The "double worsening" criterion (worsening symptoms after initial improvement) or persistent symptoms exceeding 10 days without improvement increases the suspicion for ABRS.
Indications for Specialist Referral
Referral to an Otolaryngologist or Allergist/Immunologist should be considered for:
- Recurrent acute sinusitis (≥4 episodes per year with interim resolution).
- Symptoms lasting >12 weeks, suggesting chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS).
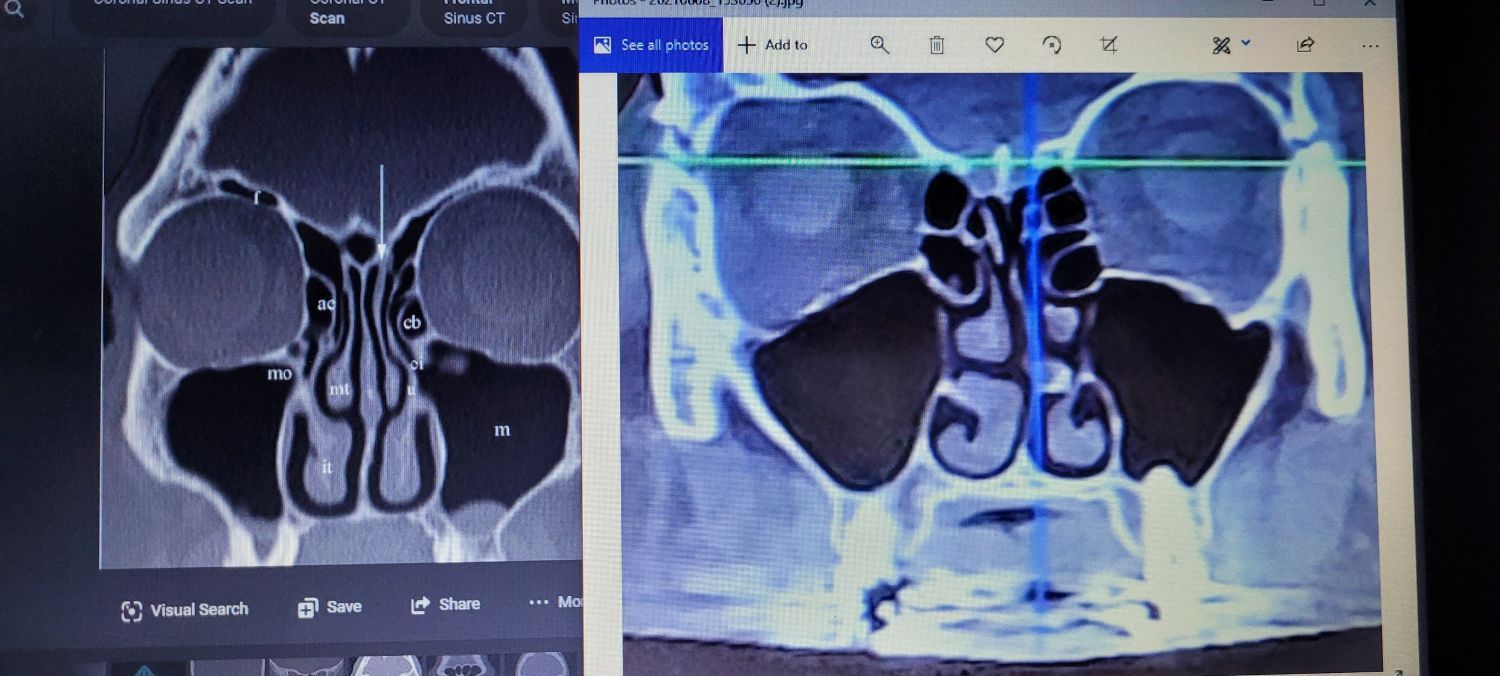
- Suspected anatomical variants (e.g., septal deviation, concha bullosa).
- Complications (e.g., periorbital swelling, severe headache, neurological signs).
- Underlying comorbidities such as allergic rhinitis, asthma, or immune deficiency requiring comprehensive management.
For the Practicing Clinician
Mastering the nuances of sinusitis management requires ongoing education. Organizations like the Snot Force Alliance provide critical platforms for specialist networking, dissemination of evidence-based treatment algorithms, and discussion of complex cases. Engaging with such professional communities is integral to advancing care for the estimated 35 million Americans affected annually.
Accurate diagnosis, judicious use of antibiotics, and timely specialist referral remain the cornerstones of effective ARS management, ultimately improving patient outcomes and curbing antimicrobial resistance.